 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
 Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Fc receptors (FcRs) are membrane molecules expressed by several hematopoietic cells that recognize the Fc region of several immunoglobulin (Ig) classes and subclasses. Immunoglobulins (Igs) are glycoproteins that have same chemical structures as antibody molecules. Igs is a tetrapeptide chain structure composed of two identical light and two identical heavy chains, connected by interchain disulfide bonds. There are five main types of Igs expressed in the human body: IgM, IgA, IgD, IgG and IgE, with the highest abundance of IgG.
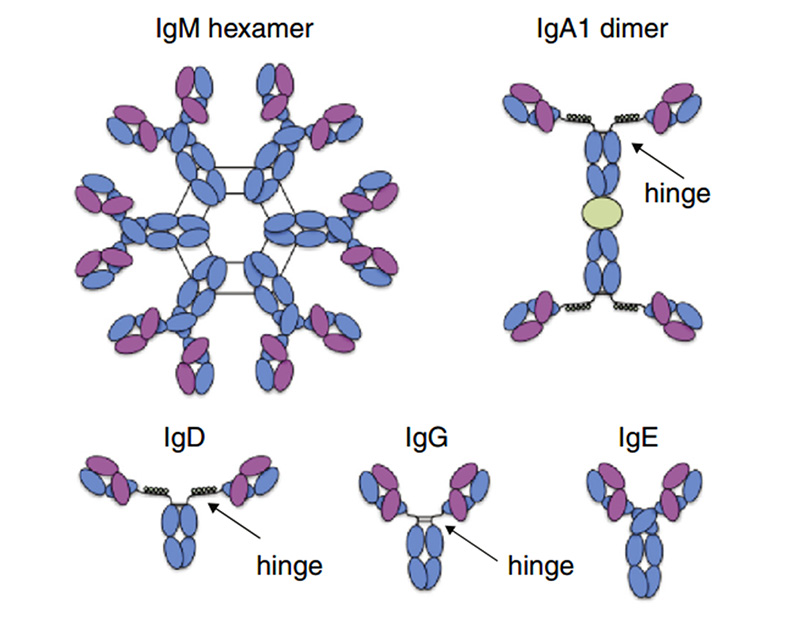 Representative Ig isotype structure
Representative Ig isotype structure
Furthermore, IgG-based antibodies are the only therapeutic antibody based products in the market at present. Communication of IgG antibodies with the immune system is controlled and mediated by Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs), membrane-bound proteins, which relay the information sensed and gathered by antibodies to the immune system.
In terms of the antibody's action mechanism, the antibody is composed of an antigen binding site (Fab) and a crystallizable site (Fc). The Fab segment can bind to a specific antigen, thereby determining the specificity and affinity of the antibody; the Fc segment of IgG can bind to Fc receptors (FcγRI, FcγRII, FcγRIII) expressed on the surface of immune cells, complement (C1q) and FcRn (neonatal FcR) in the blood, thereby activating the immune effect.
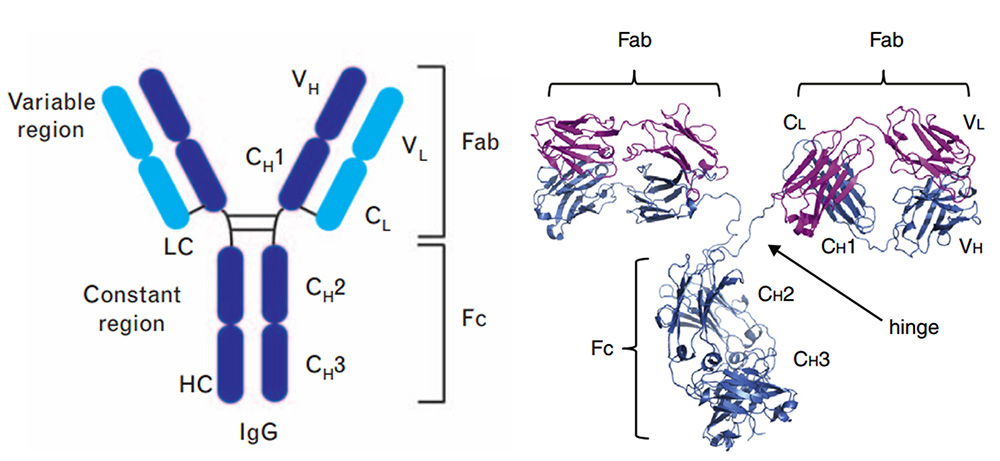 Structure of full-length IgG
Structure of full-length IgG
It is worth noting that the interaction mediated by the antibody Fc domain can strongly influence the functional outcome of antibody therapy including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) through the interaction of the Fc domain with Fc receptors on different cell types.
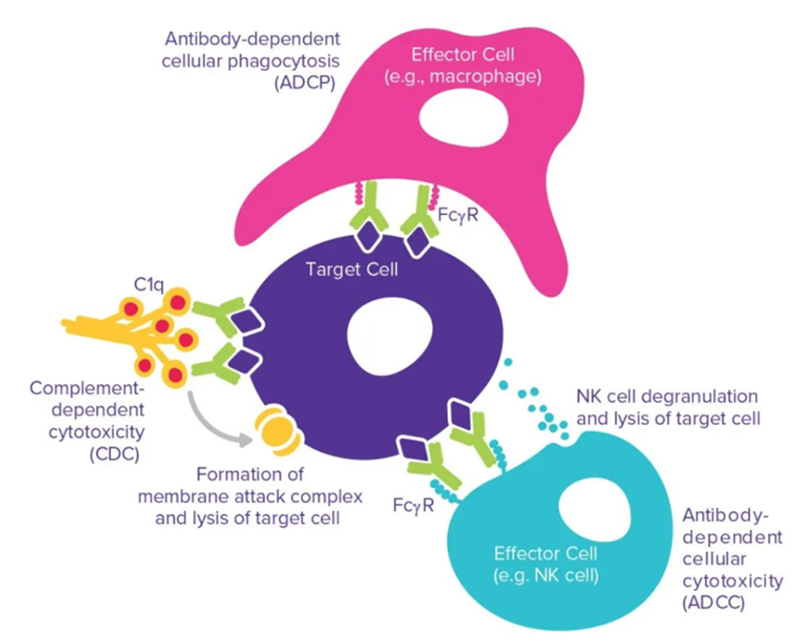
Fc-mediated interaction: ADCC, ADCP and CDC
ADCC: The antibody first binds to the target on the tumor cell, and then the Fc part is recognized by the FcγR on the effector cell. Fc and FcγR activate effector cells, leading to the release of molecules contained in cytotoxic granules, such as perforin, granulysin and granzyme, leading to the lysis of tumor cells. The ability of therapeutic antibodies to induce ADCC depends on their binding affinity to the target and activated FcγR.
ADCP: ADCP is also an important mechanism for recognizing and mediating the effect of therapeutic antibodies on tumor cells. Contrary to ADCC, ADCP mainly works by NK cells expressing FcγRIIIa. In addition, ADCP can also be expressed by monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells by expressing FcγRIIa (CD32a), FcγRI (CD64) and FcγRIIIa (CD16a) to mediate. In macrophages, the expression levels of these receptors are highly dynamic and are affected by factors such as cell, tissue microenvironment and inflammation. These three receptors can participate in antibody recognition, immune receptor aggregation, and mediate the generation of intracellular ADCP signals. Studies have shown that FcγRIIa (CD32a) is the key receptor involved in this process.
CDC: Clq component binding to Fc is a prime initial step of the complement cascade, which ultimately leads to CDC. The classical activation pathway of CDC is triggered when the C1 complex binds to the antibody-antigen complex. As the cascade of complement proteins activates, membrane attack complexes are formed, leading to the lysis of target cells. Three approved anti-cancer antibodies take advantage of this mechanism: rituximab, ofazumab (Arzerra; Genmab/GlaxoSmithKline) and tositumumab (Bexxar; GlaxoSmithKline). Several methods promote the binding of the antibody constant region to C1q successfully enhanced CDC, and engineered amino acid mutations were inserted into the Fc or hinge region, resulting in improved binding of the antibody constant region to C1q.
Half-life: The combination of IgG and neonatal FcR(FcRn) can protect antibodies from being degraded, thereby prolonging the half-life of IgG in serum. Under acidic conditions (pH6.0-6.5), FcRn binds IgG, and dissociation occurs under neutral and weakly alkaline conditions (pH7.0-7.5). Specifically, endothelial cells form endocytosis vesicles by ingesting IgG to form an acidified endosome, and IgG binds to FcRn to form an IgG-FcRn complex. The IgG-FcRn complex is transported to the cell surface through the recirculated endosome. Under physiological conditions such as pH7.4, the IgG-FcRn complex is dissociates, and the IgG is released again into the blood circulation. Through this receptor-mediated recycling mechanism, FcRn effectively protects IgG from lysosomal degradation, thus prolonging the half-life of IgG.
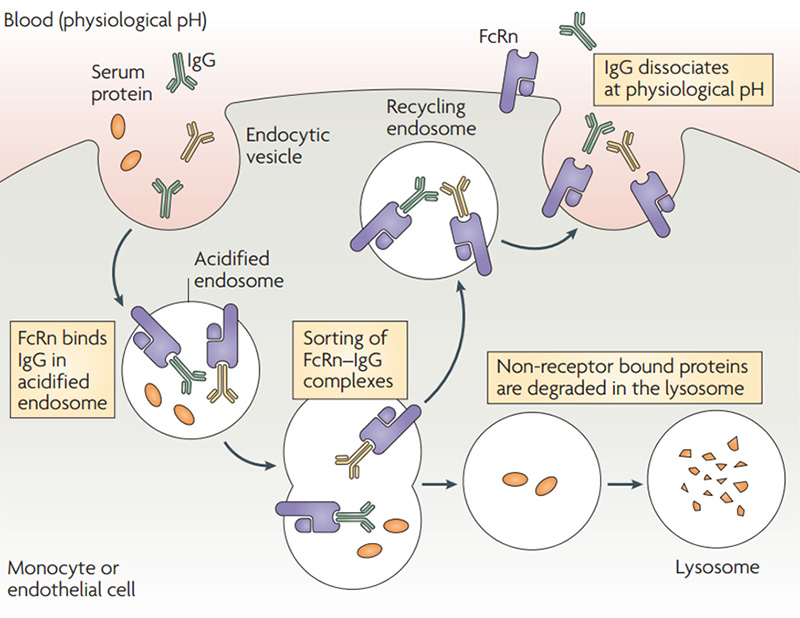 Schematic diagram of FcRn-mediated IgG and serum protein recycling
Schematic diagram of FcRn-mediated IgG and serum protein recycling
In summary, Fc receptor proteins are of great importance. The Fc domain of an antibody defines its interaction with many immune cells and has become a desired research area. With the increasing understanding of the role of Fc-FcγR, Fc-C1q and Fc-FcRn interactions, antibody engineering efforts promoted to enable exclusive functions. The activity and mechanism of therapeutic antibodies can be enhanced by choosing best Fc. For therapeutic antibody drugs, the binding affinity of candidate antibody drugs and Fc receptor proteins must be characterized to detect the biological activity of the antibody. Further, role of the antibody ADCC/ADCP/CDC/half-life should be analyzed, which has become a crucial step in the process of the development and quality control of antibody drugs.
ACROBiosystems offers a comprehensive collection of high-quality recombinant Fc receptor proteins, including their common variants, to expedite your antibody drug development.
 Expressed by HEK293 Cells: post-translational modification and proper protein folding
Expressed by HEK293 Cells: post-translational modification and proper protein folding
 Multiple species: Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rat, Porcine, Rabbit, Feline, Bovine, can be fully applied to different cross species experiments
Multiple species: Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rat, Porcine, Rabbit, Feline, Bovine, can be fully applied to different cross species experiments
 High purity: SDS-PAGE verification purity>95%, SEC-MALS verification purity>90%
High purity: SDS-PAGE verification purity>95%, SEC-MALS verification purity>90%
 Low endotoxin: <1.0 EU/µg
Low endotoxin: <1.0 EU/µg
 High stability: strict quality control to ensure high batch-to-batch consistency
High stability: strict quality control to ensure high batch-to-batch consistency
 Biotinylated Fc Receptor proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered: the labeling efficiency is high, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is suitable for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin in the process of drug development and optimization process
Biotinylated Fc Receptor proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered: the labeling efficiency is high, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is suitable for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin in the process of drug development and optimization process
 Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: activity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: activity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
FcRn
FcγR
FcεR
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FcRn (FCGRT & B2M) | FCM-H5286 | HEK293 | Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  |
| FCM-H8286 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) (SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-H82W4 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,,His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| FCM-H82W7 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) | 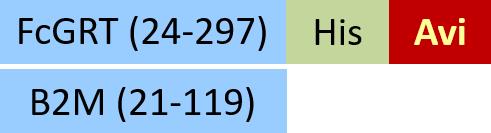 | |
| FCN-H52W7 | HEK293 | Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| FCM-M52W2 | HEK293 | Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Twin-Strep Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-M52W8 | HEK293 | Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-M82W5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-M82W6 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,,His Tag&Twin-Strep Tag (MALS & BLI-verified) |  | |
| FCM-R5287 | HEK293 | Rat FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-R82W7 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Rat FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,,His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-R52W5 | HEK293 | Rabbit FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Tag Free (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-C5284 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-C52W9 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-C82W3 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-C82W5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn Heterodimer Protein, His,&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI verified) | 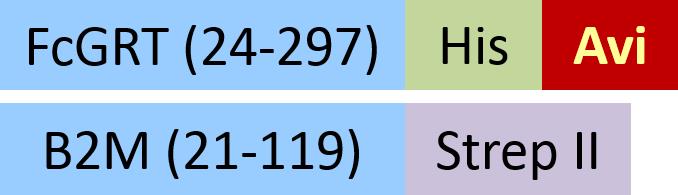 | |
| FCM-P5280 | HEK293 | Porcine FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCN-F82W3 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Feline FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCN-B82W3 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Bovine FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  |
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a | CD8-H52H4 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| CDA-H5220 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (F176) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H5290 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H52S1 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, HSA,His Tag (MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (F176) Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H82E9 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, ,His Tag (SPR & BLI verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RI / CD64 | FCA-H52H1 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  | |
| FCA-H82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | ||
| CD4-M5227 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| CD4-M82E7 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | ||
| FCA-C82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His,(MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b | CDB-M52H7 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| CDB-M82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDB-C5224 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein, His Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | ||
| CDB-C82E4 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) | 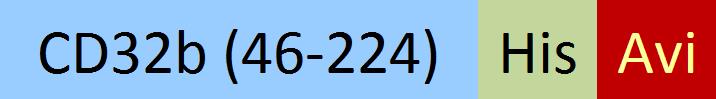 | ||
| Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c | CDB-H5228 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| CDB-H5298 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) | 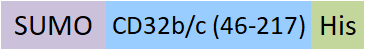 | ||
| CDB-H52S9 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein, HSA,His Tag (MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H82E0 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a | CD1-H5223 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a (H167) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| CDA-H5221 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a (R167) Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified)Hot |  | ||
| CDA-H82E6 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a (H167) Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | ||
| CDA-R52H5 | HEK293 | Rat Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | ||
| CDA-C52H7 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-C82E5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) | 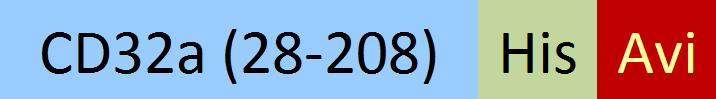 | ||
| CDA-R52H4 | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIII / CD16 | CDA-M52H8 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| FC6-M82E0 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | ||
| FC6-C52H9 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| FC6-C82E0 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His,(MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| FC6-R52H6 | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) | CDB-H5227 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) | 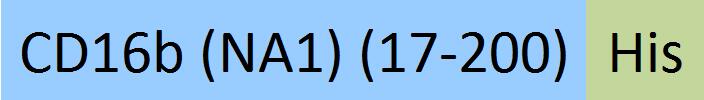 | |
| CDB-H5296 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS & BLI-verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H82E4 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) | CDB-H5222 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| CDB-H5294 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS & BLI-verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H82Ea | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIV / CD16-2 | FC4-M52H3 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RIV / CD16-2 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) | 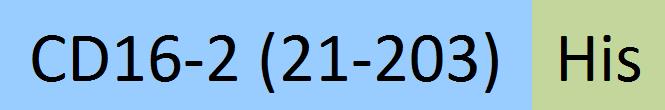 | |
| FC4-M82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RIV / CD16-2 Protein, His,(BLI verified) | 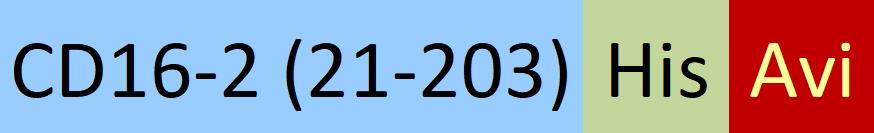 |
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD23 | CD3-H5249 | HEK293 | Human CD23 / Fc epsilon RII Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  |
| CD3-H82Q5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human CD23 / Fc epsilon RII Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | |
| Fc epsilon RI alpha | FCA-H5228 | HEK293 | Human Fc epsilon RI alpha Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  |
| FCA-H5259 | HEK293 | Human Fc epsilon RI alpha Protein, Fc Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  |
References
[1] Randall J Brezski, George Georgiou. Immunoglobulin isotype knowledge and application to Fc engineering. Current Opinion in Immunology 2016, 40:62–69.
[2] Derry C. Roopenian, Shreeram Akilesh. FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2007,7:715–725.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
