
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
 Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
> Insights > Binding and neutralizing antibodies correlated with COVID-19 risk and vaccine efficacy It is common sense that COVID-19 vaccines protect the human body against SARS-CoV-2 infection by inducing immune response. Theoretically, the stronger the immune response, the better a person is protected. However, the specific “immune correlate” of vaccine protection has never been confirmed owning to the lack of scientific verification. This hypothesis is lately proven true by an analysis of the Coronavirus Efficacy (COVE) trial (NCT04470427) of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine mRNA-1273, which is jointly undertaken by researchers at Moderna, NIH VRC and Fred Hutchinson Institute, and published on medRxiv.
This study provides the strongest evidence to date that high levels of vaccine-elicited binding and neutralizing antibodies translate to low risk of COVID-19 infection and high level of vaccine protection over time. The team finds that 1) 57 days after the first dose of mRNA-1273 (=4 weeks after the second dose), the vaccine-induced RBD and S-specific IgG, as well as the serum neutralization titer in human, are inversely correlated with the occurrence of COVID-19 cases. 2) Importantly, vaccine recipients with higher Day 57 cID50 (50% inhibitory dilution pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titers) have lower risk of infection in the next 100 days. For individuals with cID50 titer level that is undetectable, 100, or 1000, the cumulative incidence of COVID-19 was 0.03, 0.0056, and 0.0023, respectively; the corresponding vaccine efficacy was 50.8% (may be contributed by T cells response), 90.7% and 96.1%. In conclusion, these findings provide scientific support for measuring neutralizing antibody titer as the marker of vaccine protection.
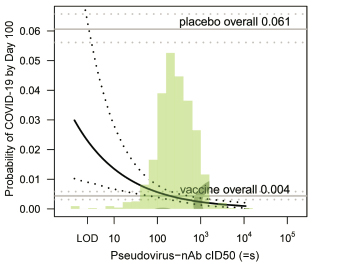 Fig 1. Cumulative incidence of COVID-19 by 100 days post Day 57 by Day 57 cID50 level.
Fig 1. Cumulative incidence of COVID-19 by 100 days post Day 57 by Day 57 cID50 level.
As demonstrated by this study, viral pseudotypes provide reliable estimations of the neutralizing activity of serological samples. Alternatively, a protein-based competitive ELISA assay can be utilized, which is easier to manipulate and more feasible for scale-up in routine vaccine production and quality control.
Peter B. Gilbert, David C. Montefiori, Adrian McDermott, et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial. medRxiv 2021.08.09.21261290; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.09.21261290
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.







