
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
 Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
The massive spread of SARS-CoV-2 Lambda (C.37 lineage) in South American countries has contributed to its recent declaration as global VOI by the WHO (Figure 1). Since its initial identification in Nov 2020, the Lambda variant has expanded rapidly in Peru, Chile and Argentina in the presence of hundreds of circulating lineages, and appears to have replaced the highly transmissible Alpha variant (B.1.1.7 lineage) in some densely populated regions.
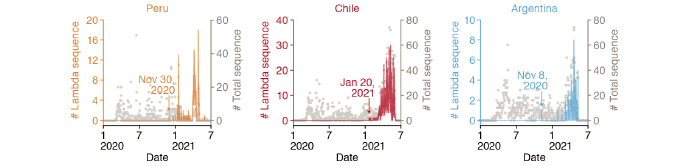
Fig 1. Epidemic dynamics of the Lambda variant in three South American countries1.
Characterized by a unique 7-amino acid deletion (S:Δ247-253, located at the N-terminal domain) and six nonsynonymous mutations in the spike gene (G75V, T76I, L452Q, F490S, D614G, T859N) (Figure 2) 2, 3, the SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant display a novel mutation pattern that requires close investigation2.
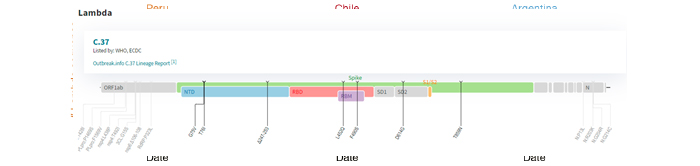
Fig 2. Mutations identified on the Lambda variant3.
The Lambda variant is associated with higher risk of developing severe symptoms and substantial reduction in neutralizing activity of monoclonal antibodies, convalescent and vaccine sera. Researchers at NYU have demonstrated with pseudovirus assays that lambda spike caused a 3-fold increase in ACE2 binding, which underlies its high infectivity. In the same study, the lambda spike showed 3.3-fold, 3-fold, and 2.3-fold resistance to neutralization by convalescent sera, Pfizer BNT162b2 and Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccinee serum, respectively, as compared to neutralization of virus with the parental D614G spike (Figure 3)4.
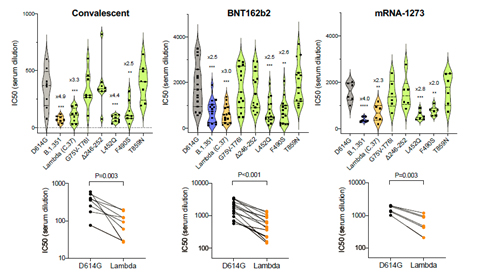
Fig 3. The Lambda spike shows partial resistance to neutralization by convalescent sera and vaccine-elicited sera (Pfizer BNT162b2 and Moderna mRNA-1273).
Preliminary studies show that the increased infectivity and resistance of Lambda were likely attributed to the L452Q and F490S mutations on RBD as well as the large deletions on NTD “supersite”. Further research is needed to determine how the mutations specifically impact the dynamics, severity and immune breakthrough of this new variant of interest.
In order to support the fight against SARS-CoV-2 variants, ACROBiosystems is accelerating the development of recombinant S and N antigens with the Lambda mutations. The Lambda spike trimer protein was verified by SDS-PAGE and SEC-MALS with high purity (more than 90%).
| Cat.No. | Tag | Product description | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPN-C52Hs | His Tag | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Trimer (G75V, T76I, SYLTPGD 247-253 del, L452Q, F490S, D614G, T859N), His Tag (MALS verified) | |
| SPD-C5227 | His Tag | SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD (L452Q, F490S), His Tag | |
| SPD-C82Eh | His Tag & Avi Tag | Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD (L452Q, F490S), His,Avitag™ | |
| NUN-C52Ha | His Tag | SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein (P13L, R203K, G204R, G214C), His Tag |
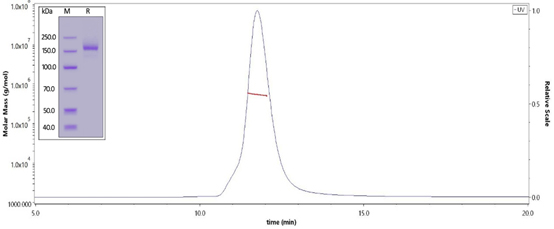
The purity of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Trimer, His Tag (Cat. No. SPN-C52Hs) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 540-595 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Izumi Kimura, Yusuke Kosugi, Jiaqi Wu, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant exhibits higher infectivity and immune resistance. bioRxiv 2021.07.28.454085; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.28.454085.
Pedro E. Romero, Alejandra Dávila-Barclay, Guillermo Salvatierra, et al. The Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Lambda (C.37) in South America. medRxiv 2021.06.26.21259487; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.26.21259487
Takuya Tada, Hao Zhou, Belinda M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 Lambda Variant Remains Susceptible to Neutralization by mRNA Vaccine-elicited Antibodies and Convalescent Serum. bioRxiv 2021.07.02.450959; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.02.450959
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.







