 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
 Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
> Insights > 【Inspiring Target】Therapeutic potential of IL-6 immunization in multiple fields continues to burst In terms of disease, IL-6 can have local inflammatory and systemic inflammatory effects and is related to the pathogenesis of various diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD), giant cell arteritis (GCA), Castleman disease, and cytokine release syndrome (CRS), as well as other conditions. IL-6 has multiple roles in the dysfunction of the immune and inflammatory systems, and anti-IL-6 treatment can relieve various symptoms such as fever, fatigue, pain, joint destruction, and anemia.
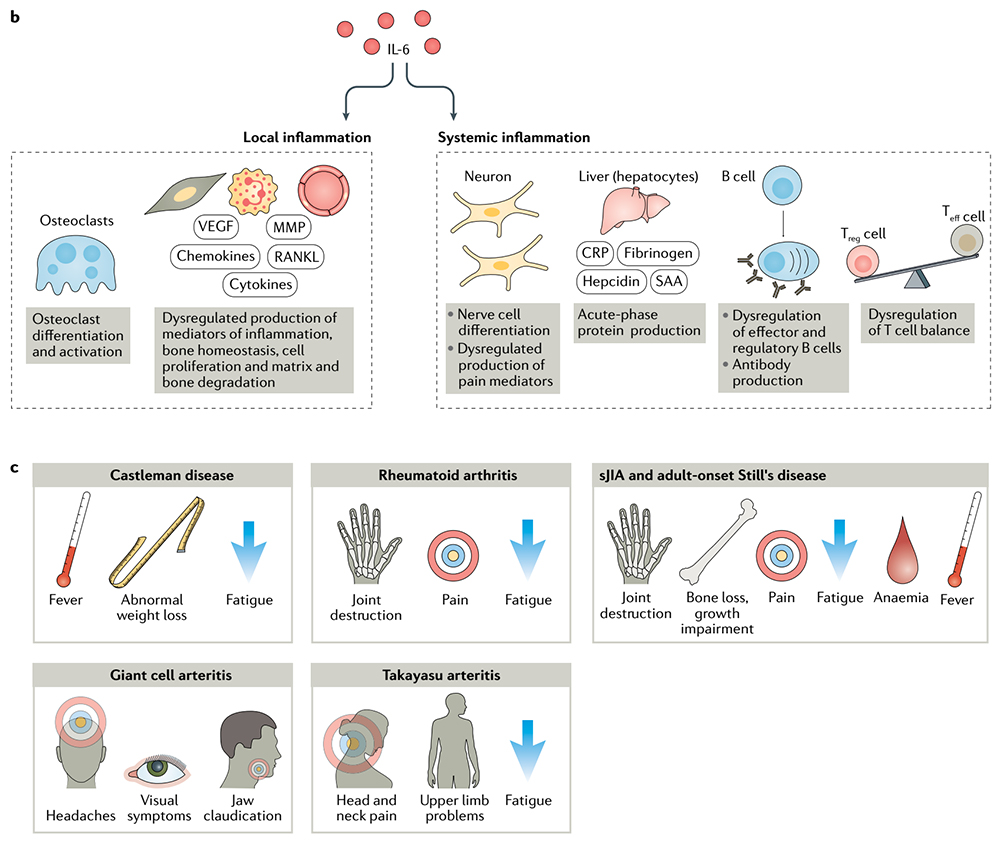
IL-6 has multiple roles in dysfunction of the immune and inflammatory systems
When the research team found that IL-6 signaling is mediated through a high-affinity complex of IL-6, IL-6R, and gp130 hexamer, the traditional approach to finding small-molecule inhibitors proved challenging. Therefore, targeting IL-6 or IL-6R, blocking the binding of IL-6 and IL-6R, thereby inhibiting IL-6 pathway signal transduction, this IL-6 pathway inhibitor opens a new journey as a variety of diseases potential treatments. Initially, taking into consideration that concentrations of the receptor have less interpatient variability than concentrations of IL-6, potentially simplifying dose and regimen selection, the researchers decided to target IL-6R rather than IL-6 itself.
Tocilizumab is the first humanized monoclonal antibody targeting IL-6R, which inhibits IL-6 signaling by preventing IL-6 from binding to IL-6R. It has been approved for multiple indications including: RA, pJIA, sJIA, GCA, CRS, Takayasu arteritis (TA). Tocilizumab includes intravenous (IV) and subcutaneous (SC) formulations, and specific indications vary by country and region. In China, its IV formulation has been approved for the treatment of RA, sJIA, and CRS. In March 2021, FDA approved a new indication for Tocilizumab to slow the rate of lung function decline in adult patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
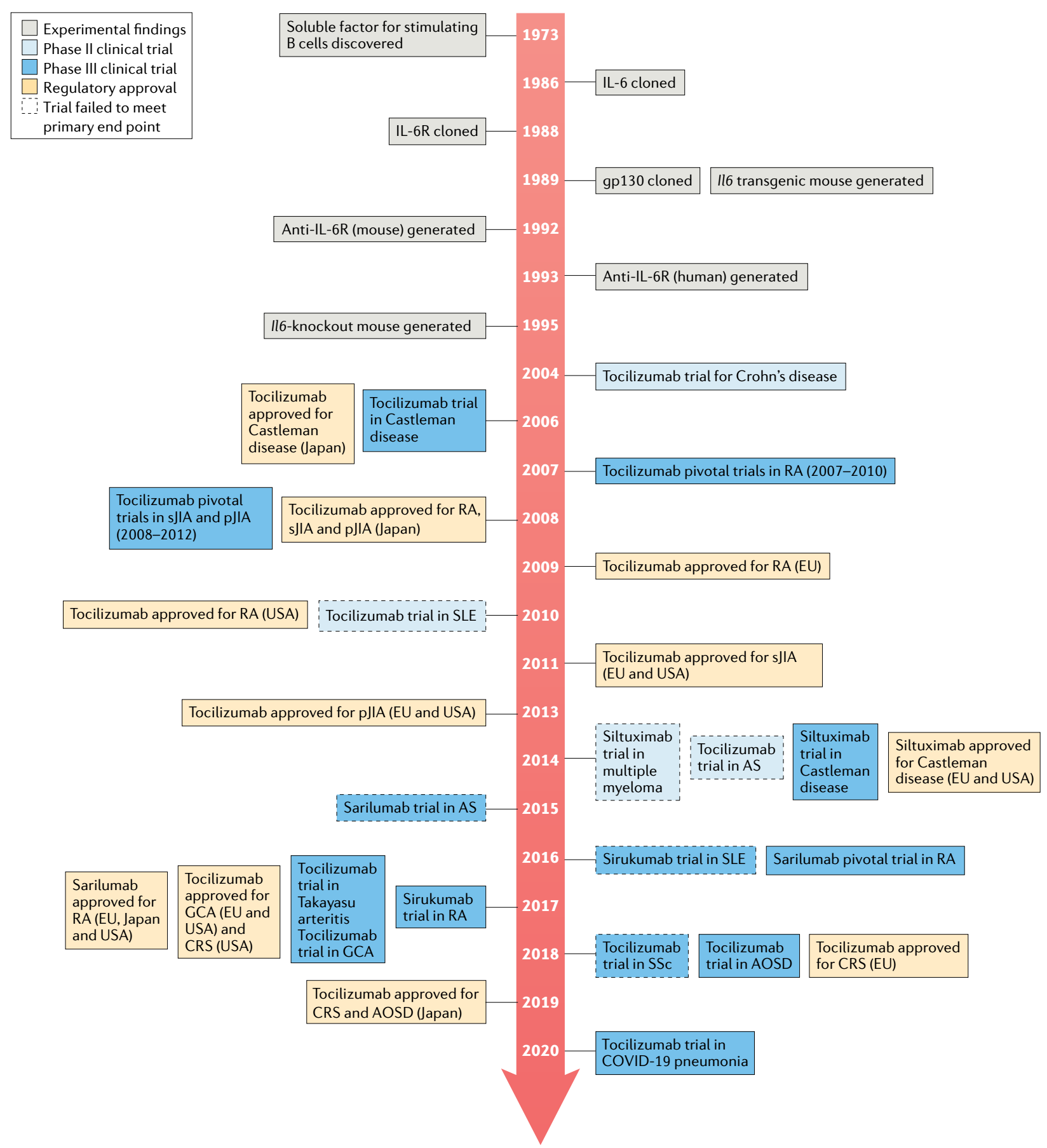
Advances in IL-6 and IL-6R targeted drugs
Tocilizumab was approved by the FDA and EMA in 2017 and 2018, respectively, for the treatment of severe or life-threatening CAR-T cell therapy-induced CRS in adults and children (approximately 70% of patients treated with CD19 CAR-T cells will develop CRS. CRS can cause headache, fever, chills, severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, difficulty breathing, hypotension, and tachycardia, which can be fatal in severe cases). Approval for this indication is based on data from a retrospective analysis showing the efficacy of Tocilizumab treatment in patients with CRS following CAR-T cell therapy in a prospective clinical trial.
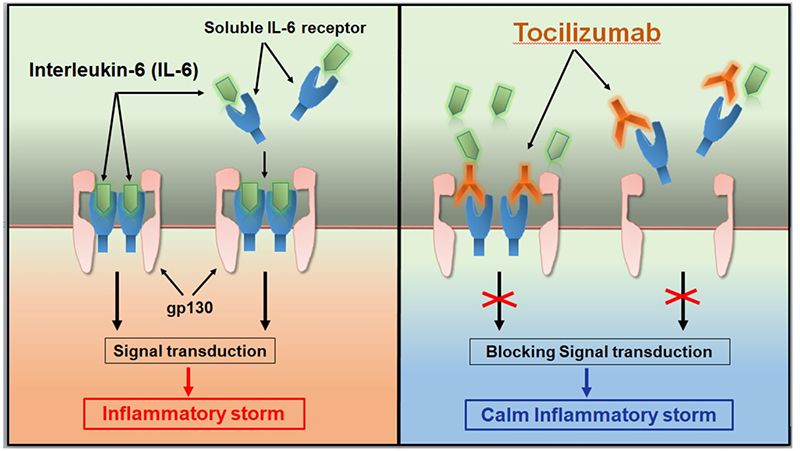
Tocilizumab calms the inflammatory storm
The therapeutic benefit of Tocilizumab, an IL-6R antibody, has led to the development of several IL-6-targeting antibodies, such as Sirukumab, Olokizumab, and Clazakizumab, however, indications vary between them.
Previous retrospective studies suggested that the progression of the COVID-19 epidemic may be due to CRS, and the potential role of IL-6 in severe COVID-19 patients was revealed. The dramatic increase in the levels of IL-6 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines (eg, IL-1, IL-8, IL-12) plays a key role in the worsening health status of COVID-19 patients. Pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes with high IL-6 secretion may enter the pulmonary circulation in large numbers, incite the inflammatory storm and lead to an immune disorder in severe COVID-19 patients. It may cause severe pneumonia to develop into acute respiratory distress syndrome, cause immune dysfunction and eventually lead to multisystem organ failure and even high mortality. In conclusion, elevated IL-6 concentrations constitute a larger cytokine storm that exacerbates disease outcomes. Therefore, IL-6 is a potential therapeutic target for critical cases of COVID-19.
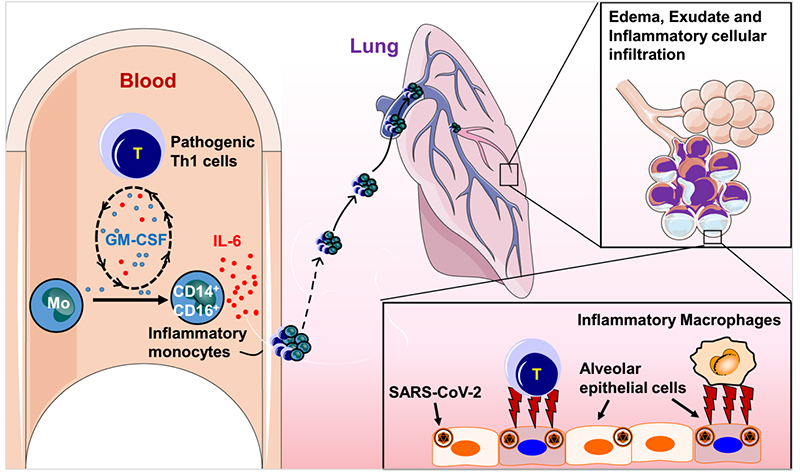
The pivotal role of IL-6 in the progression of COVID-19 patients
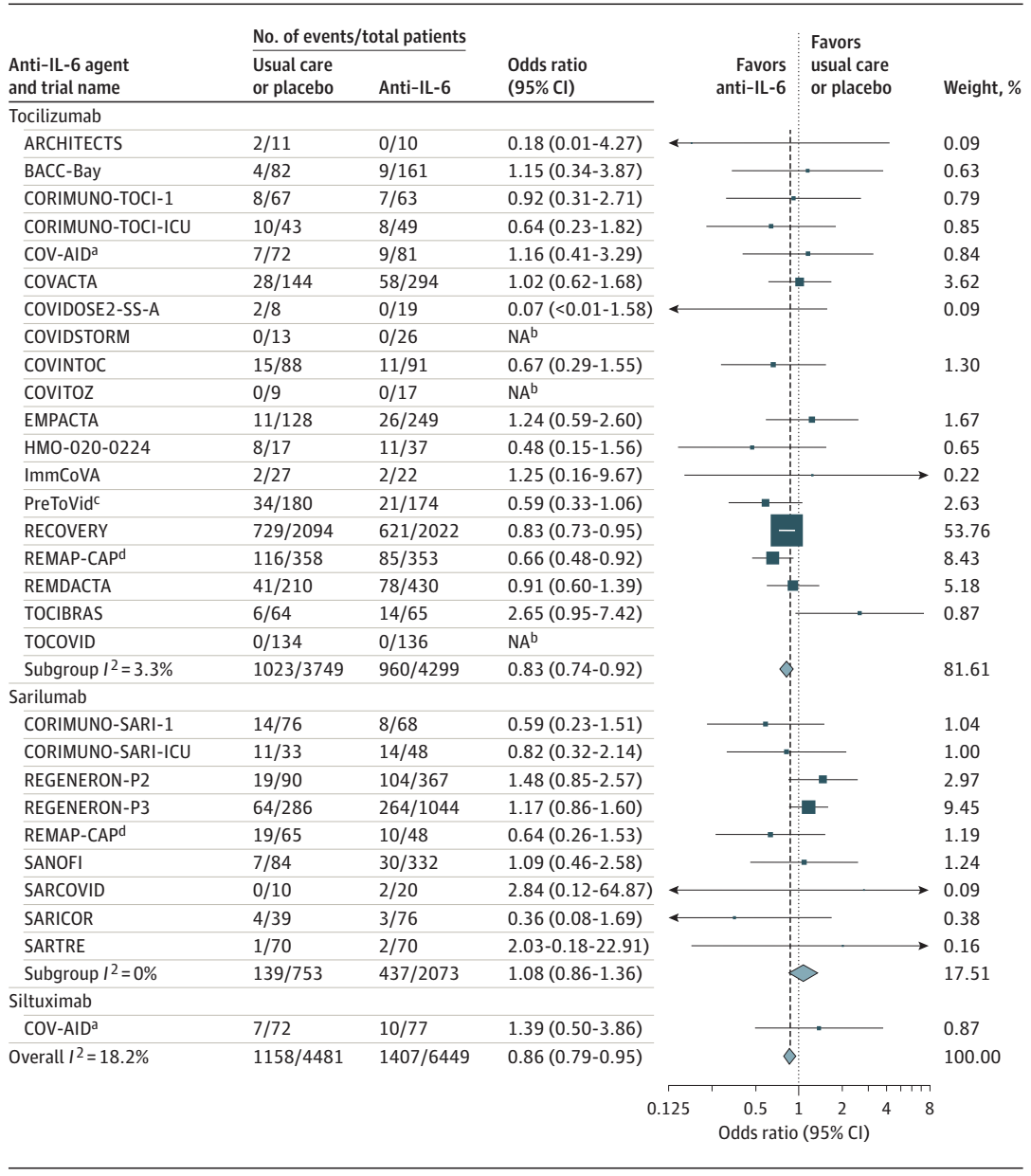
The World Health Organization (WHO) Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group developed a prospective meta-analysis protocol to perform a prospective meta-analysis of IL-6 antagonists in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. 72 potentially eligible trials were identified through systematic searches of ClinicalTrials.gov, the EU Clinical Trials Register, and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform from October 7, 2020, to January 11, 2021, of which 27 (37.5 %) met the study selection criteria. Eligible trials randomly assigned patients hospitalized for COVID-19 to a group in whom IL-6 antagonists were administered and to a group in whom neither IL-6 antagonists nor any other immunomodulators except corticosteroids were administered. A total of 10 930 patients (median age, 61 years) participating in 27 trials were included. The primary outcome measure was all-cause mortality at 28 days after randomization.
By 28 days, there were 1407 deaths among 6449 patients randomized to IL-6 antagonists and 1158 deaths among 4481 patients randomized to usual care or placebo (summary OR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.79-0.95]; P =0.003 based on a fixed-effects meta-analysis). This corresponds to an absolute mortality risk of 22% for IL-6 antagonists compared with an assumed mortality risk of 25% for usual care or placebo. The corresponding summary ORs were 0.83 (95% CI, 0.74-0.92; P < .001) for Tocilizumab and 1.08 (95% CI, 0.86-1.36; P = .52) for Sarilumab. The summary ORs for the association with mortality compared with usual care or placebo in those receiving corticosteroids were 0.77 (95% CI, 0.68-0.87) for Tocilizumab and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.61-1.38) for Sarilumab. In this prospective meta-analysis for clinical trials of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, the use of IL-6 antagonist was associated with a reduction in 28-day all-cause mortality compared with usual care or placebo.
Targeting the IL-6 pathway opens up innovative treatments for a variety of rheumatic diseases. Emerging evidence suggests that dysregulation of IL-6 contributes to a variety of disease states, including various types of cancer development, progression, and metastasis, increased levels of IL-6 are associated with a higher risk of cancer and other diseases, such as insulin resistance, asthma, coronary heart disease, advanced cancer, and can also serve as a prognostic marker for cancer. Targeting this pathway may expand to the treatment of several other symptoms, such as uveitis, neuromyelitis optica, and more recently, COVID-19 pneumonia.
However, the journey to realize the therapeutic potential based on the IL-6 pathway is far from over since there some questions related to IL-6 biology need to be answered. For example, why are IL-6 levels elevated, and why IL-6 signaling inhibition produces clinically meaningful benefits in patients with some diseases such as RA, but not all diseases associated with excess IL-6 levels? Answering these questions will help us further understand how the IL-6 signaling pathway regulates various autoimmune diseases and will help to develop more, personalized treatment options for individual patients or patient subgroups.
ACROBiosystems has developed a series of high-quality IL-6 and IL-6 receptor proteins to facilitate the development of IL-6 related drugs.
![]() Human and Mouse species are available
Human and Mouse species are available
![]() High purity:>95%
High purity:>95%
![]() High bioactivity verified by ELISA, BLI and cell-based assay. Free protocols offered
High bioactivity verified by ELISA, BLI and cell-based assay. Free protocols offered
![]() Various tags:Tag Free,His Tag,Avi & His Tag,Fc Tag
Various tags:Tag Free,His Tag,Avi & His Tag,Fc Tag
![]() Low endotoxin:< 1.0 EU/μg
Low endotoxin:< 1.0 EU/μg
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | IL6-H8218 | Human | Biotinylated Human IL-6 Protein, epitope tag free, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) | |
| IL-6 | IL6-H4218 | Human | ActiveMax® Human IL-6 Protein, Tag Free | |
| IL-6 | IL6-M5245 | Mouse | Mouse IL-6 Protein, His Tag | |
| IL-6 | IL6-M82Q7 | Mouse | Biotinylated Mouse IL-6 Protein, Avitag™,His Tag | |
| IL-6 R alpha | ILR-H4223 | Human | Human IL-6 R alpha / CD126 Protein, His Tag | |
| IL-6 R alpha | CD6-H82E8 | Human | Biotinylated Human IL-6 R alpha / CD126 Protein, Avitag™,His Tag | |
| IL-6 R alpha | ILR-H5259 | Human | Human IL-6 R alpha / CD126 Protein, Fc Tag | |
| IL-6 R alpha | ILR-M82E9 | Mouse | Biotinylated Mouse IL-6 R alpha / CD126 Protein, His,Avitag™ | |
| gp130 | ILT-M52H1 | Mouse | Mouse gp130 / CD130 / IL-6 R beta Protein, His Tag | |
| gp130 | ILT-M5252 | Mouse | Mouse gp130 / CD130 / IL-6 R beta Protein, Fc Tag |
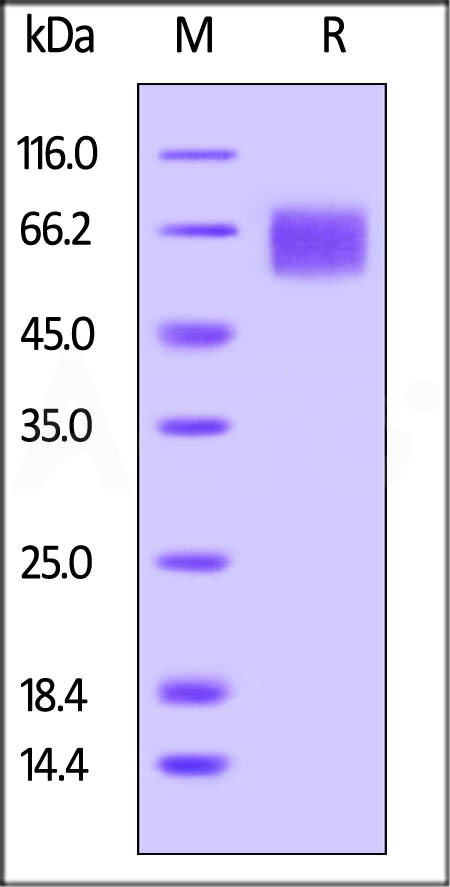

Biotinylated Human IL-6 R alpha, Avitag, His Tag (Cat. No. CD6-H82E8) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained overnight with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%. The protein has a calculated MW of 41.7 kDa and migrates as 55-70 kDa due to glycosylation.
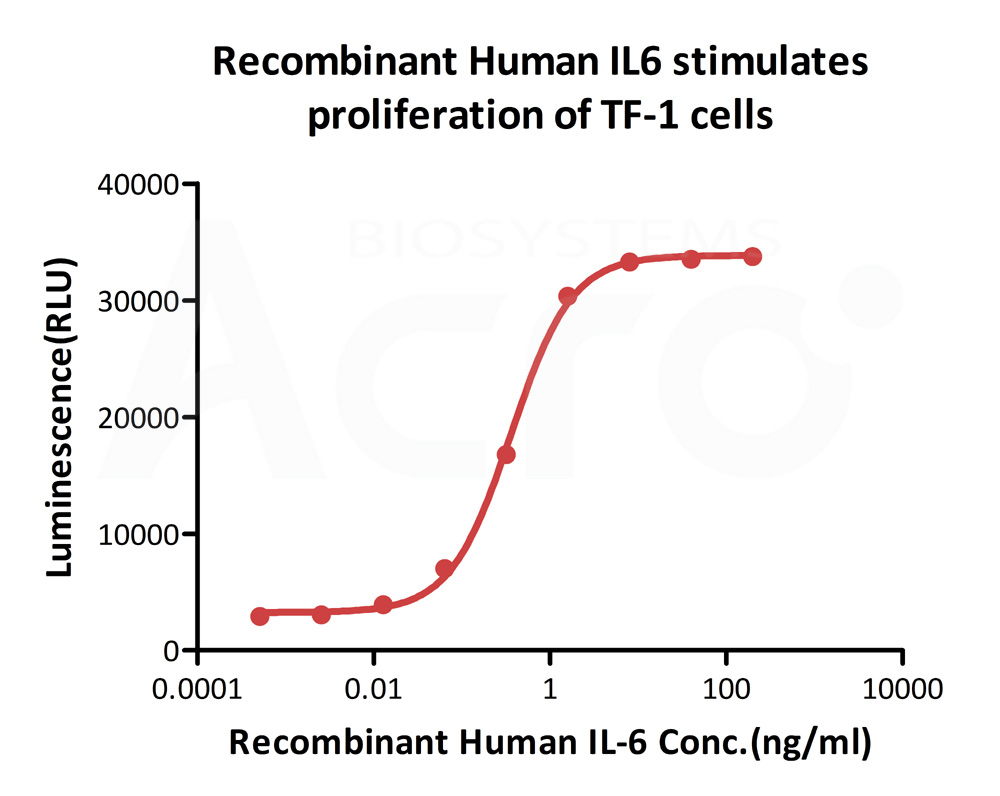
ActiveMax® Human IL-6, Tag Free (Cat. No. IL6-H4218) stimulates proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cell line. The EC50 for this effect is 0.2856-0.3636 ng/mL.
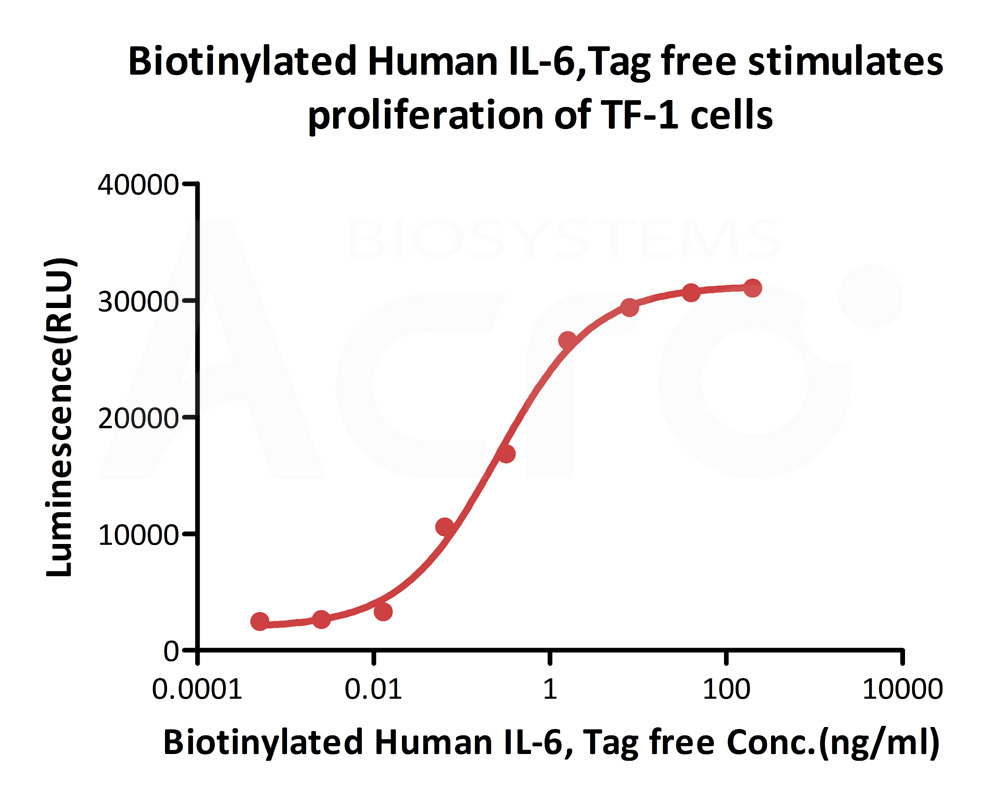
Biotinylated Human IL-6, epitope tag free, primary amine labeling (Cat. No. IL6-H8218) stimulates proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cell line. The EC50 for this effect is 0.2532-0.4489 ng/mL.
Authors:Choy, E.H., De Benedetti, F., Takeuchi, T. et al.
Authors:Atal, S., Fatima, Z.
Authors:Anjali Dhall et al.
Authors: The WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group.
Authors:Fu, B., Xu, X. & Wei, H.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
