 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Fc receptors (FcRs) are a group of glycoproteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily and are organized into classes, such as Fc alpha receptors (FcαRs), Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) and Fc epsilon receptors (FcεRs). Communication of IgG antibodies with the immune system is controlled and mediated by FcγRs, which relay the information sensed and gathered by antibodies to the immune system. IgG is the most studied and best characterized of the Igs and is divided into four distinct subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4), each with differences in sequence and structure, binding properties to FcγRs and effector functions.
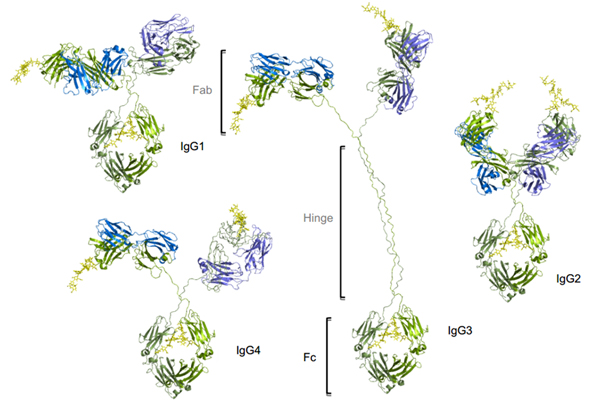 Figure1. Four subtypes of IgG exist in humans: IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4. Conserved Asn 297 amino acids in the Fc region with N-glycans attached (shown in yellow), Heavy chains are shown in green, and light chains are shown in blue and purple.
Figure1. Four subtypes of IgG exist in humans: IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4. Conserved Asn 297 amino acids in the Fc region with N-glycans attached (shown in yellow), Heavy chains are shown in green, and light chains are shown in blue and purple.
The four subtypes are named based on their respective abundance in serum with IgG1 being the most abundant. IgG antibodies consist of two Fab regions that can bind both an antigen molecule and the Fc region which interact with the FcγRs, joined by a highly flexible hinge region. IgG1 has the highest affinity to all FcγRs, leading to significant effector functions, such as ADCC, ADCP, and CDC. Although human IgG3 can also mediate competent effector functions, it has a very long hinge region and complex disulfide bonds, resulting in significantly greater polymorphism, which may increase the risk of immunogenicity. Therefore, the IgG3 isotype is rarely chosen in antibody therapeutics. In comparison, IgG2 and IgG4 induce significantly weaker or no ADCC and CDC.
Based on the differences in structure, function, and affinity for IgG binding, FcγRs are classified into three major groups: FcγRI/CD64, FcγRII/CD32 (FcγRIIa, FcγRIIb and FcγRIIc) and FcγRIII/CD16 (FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIIb). Among them, FcγRI, FcγRIIa, and FcγRIIIa are activating receptors containing the signal transduction motif, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), in the γ subunit of FcγRI and FcγRIIIa, or in the cytoplasmic tail of FcγRIIa. In contrast, FcγRIIb is an inhibitory receptor. Cross-linking of FcγRIIb leads to the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and inhibitory signaling transduction.
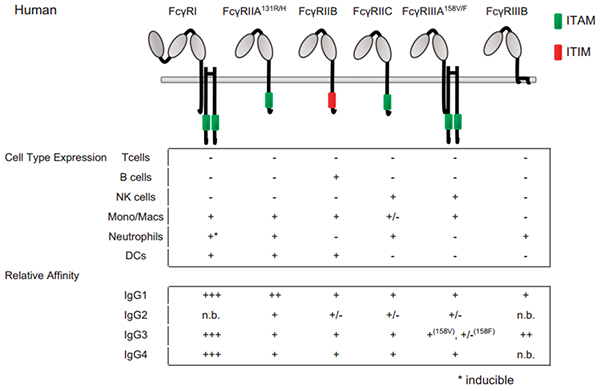 Figure 2 Fc–FcγRs interactions and FcγRs expression across cell subsets in human.
For cell-type expression, + indicates constitutive expression, +* indicates inducible expression and − indicates no expression. For relative affinities, +++ indicates lower than 1 μM, ++ indicates 1–10 μM, + indicates 10–100 μM, +/− indicates higher than 100 μM and n.b. indicates no binding. †Indicates binding observed with no affinity reported.
Figure 2 Fc–FcγRs interactions and FcγRs expression across cell subsets in human.
For cell-type expression, + indicates constitutive expression, +* indicates inducible expression and − indicates no expression. For relative affinities, +++ indicates lower than 1 μM, ++ indicates 1–10 μM, + indicates 10–100 μM, +/− indicates higher than 100 μM and n.b. indicates no binding. †Indicates binding observed with no affinity reported.
FcγRI is a high-affinity Fc receptor for both the monomeric IgG and immune complex (IC). The affinities of FcγRI to IgG1 or IgG4 are similar (1–10 nM KD). In contrast, FcγRI has no binding to IgG2. FcγRI is mainly expressed on monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), and activated neutrophils. One of the major functions of FcγRI is to activate myeloid cells to phagocytose IgG1 and IgG-bound target cells via ADCP. Due to high-affinity binding of FcγRI to monomeric IgG and high serum concentrations of IgG (∼15 mg/mL), it is believed that most FcγRI is occupied by endogenous IgG. However, a recent study has shown that stimulation of myeloid cells with cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ), could induce the clustering of FcγRI and increase the binding of FcγRI to ICs. Multiple studies have also shown that FcγRI plays an important role in modulating immune responses in autoimmune diseases, inflammation, and antibody therapy.
FcγRII is the receptor most widely expressed on hematopoietic cells among FcγRs. FcγRII includes FcγRIIA, FcγRIIB and FcγRIIC isoforms. FcγRIIA, expressed on monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and platelets is more largely expressed on immune cells than FcγRIIC that has been identified on NK cells. FcγRIIA initiates endocytosis, phagocytosis, ADCC, and inflammatory mediator release. By contrast, FcγRIIB, expressed on B cells, basophils, mast cells, monocytes, macrophages and DC transduce inhibitory signals that down-regulate immune functions triggered by activating receptors, when co-ligated with the latter receptors.
Two different FcγRIII isoforms have been identified. FcγRIIIB is a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored- FcγRIIIB expressed on neutrophils and involved in degranulation and generation of reactive oxygen intermediates by these cells. FcγRIIIA is a transmembrane isoform expressed on NK cells and a small subpopulation of T lymphocytes as well as on monocytes and macrophages, although at low levels in the latter case. FcγRIIIA is involved in ADCC, phagocytosis, endocytosis and cytokine release.
While the mouse IgG system differs from the human in important ways (mice express IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3, all with different affinities for mouse FcγRs compared with human), with higher affinity Fc–FcγRs engagement by the mouse IgG2a isotype for activating FcγRs than that of human IgG1.
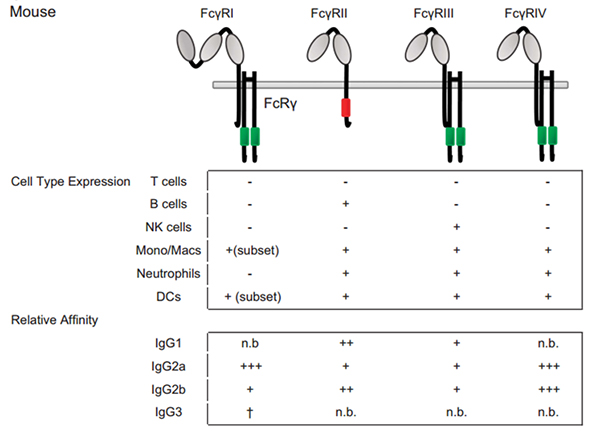 Figure 3 Fc–FcγRs interactions and FcγRs expression across cell subsets in mouse.
For cell-type expression, + indicates constitutive expression, +* indicates inducible expression and − indicates no expression. For relative affinities, +++ indicates lower than 1 μM, ++ indicates 1–10 μM, + indicates 10–100 μM, +/− indicates higher than 100 μM and n.b. indicates no binding. †Indicates binding observed with no affinity reported.
Figure 3 Fc–FcγRs interactions and FcγRs expression across cell subsets in mouse.
For cell-type expression, + indicates constitutive expression, +* indicates inducible expression and − indicates no expression. For relative affinities, +++ indicates lower than 1 μM, ++ indicates 1–10 μM, + indicates 10–100 μM, +/− indicates higher than 100 μM and n.b. indicates no binding. †Indicates binding observed with no affinity reported.In mice, only FcγRI, FcγRIIB, and FcγRIIIA human equivalents have been described. Mouse FcγRI and FcγRIIIA (termed FcγRIII) exhibit the same activating properties as their human counterparts. These two mouse receptors bind IgG with a high and a low affinity, respectively. Mouse FcγRIIB (termed FcγRII) is also a low affinity receptor that exhibits inhibitory functions as the human FcγRIIB that contains an ITIM. All mouse FcγRs can bind human IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses, in addition to mouse IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b subclasses. Among these subclasses, IgG2a is a strong binder of FcγRI, as compared to IgG1 and IgG2b which preferentially bind FcγRIIB and FcγRIII, to which IgG2a also binds. Whether a specific mouse Fc receptor for mouse IgG3 exists is still a matter of controversy, although it has been claimed that this subclass could bind mouse FcγRI.
FcγRs are expressed mostly on leukocytes and they are the class of receptors most relevant for the function of therapeutic antibodies. FcγRs are divided into three types, FcγRI (CD64), FcγRII (CD32) and FcγRIII (CD16). They have traditionally been categorized according to their affinity for specific IgG subclasses and the type of signaling pathway that they trigger; that is, whether it is inhibitory or activating. In general, FcγRI has been considered to be a high-affinity receptor that binds both monomeric IgG and immune complexes, whereas the affinity of FcγRII and FcγRIII for IgGs is low and intermediate, respectively.
Engineering the Fc region of IgG mAbs or IgG-like bispecific antibodies to modulate IgG/FcγRs interactions is a major goal of current studies on therapeutic antibodies. The development and manufacture of therapeutic antibodies, including Fc (crystallizable fragment) fusion proteins, represent a significant segment of the biopharmaceutical industry and have resulted in substantial benefits to public health. In conclusion, binding of the antibody Fc-hinge region to FcγRs has been shown to exert a profound impact on antibody function and in vivo efficacy.
ACROBiosystems offers a comprehensive collection of recombinant Fc receptor proteins, including their common variants, to expedite your antibody drug development.
The use of biotin labeling can make your assay development much easier. We offer a variety of “ready-to-use” biotinylated Fc receptors. These proteins are produced using our in-house developed labeling techniques, which confers high bioactivity and minimal batch-to-batch variation. In addition, we have developed a series of Fc receptors of other species, which are suitable for the screening of non-humanized antibodies or the species cross reaction.
 Expressed by HEK293 Cells: post-translational modification and proper protein folding
Expressed by HEK293 Cells: post-translational modification and proper protein folding
 Multiple species: Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rat, Porcine, Rabbit, Feline, Bovine, can be fully applied to different cross species experiments
Multiple species: Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rat, Porcine, Rabbit, Feline, Bovine, can be fully applied to different cross species experiments
 High purity: SDS-PAGE verification purity>95%, SEC-MALS verification purity>90%
High purity: SDS-PAGE verification purity>95%, SEC-MALS verification purity>90%
 Low endotoxin: <1.0 EU/µg
Low endotoxin: <1.0 EU/µg
 High stability: strict quality control to ensure high batch-to-batch consistency
High stability: strict quality control to ensure high batch-to-batch consistency
 Biotinylated Fc Receptor proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered: the labeling efficiency is high, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is suitable for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin in the process of drug development and optimization process
Biotinylated Fc Receptor proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered: the labeling efficiency is high, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is suitable for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin in the process of drug development and optimization process
 Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: activity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: activity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
FcRn
FcγR
FcεR
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FcRn (FCGRT & B2M) | FCM-H5286 | HEK293 | Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  |
| FCM-H8286 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) (SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-H82W4 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,,His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| FCM-H82W7 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCN-H52W7 | HEK293 | Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| FCM-M52W2 | HEK293 | Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Twin-Strep Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-M52W8 | HEK293 | Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-M82W5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-M82W6 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,,His Tag&Twin-Strep Tag (MALS & BLI-verified) |  | |
| FCM-R5287 | HEK293 | Rat FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-R82W7 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Rat FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,,His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-R52W5 | HEK293 | Rabbit FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Tag Free (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-C5284 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-C52W9 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-C82W3 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCM-C82W5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FcRn Heterodimer Protein, His,&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI verified) |  | |
| FCM-P5280 | HEK293 | Porcine FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCN-F82W3 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Feline FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  | |
| FCN-B82W3 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Bovine FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His,(MALS & SPR verified) |  |
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a | CD8-H52H4 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| CDA-H5220 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (F176) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H5290 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H52S1 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, HSA,His Tag (MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (F176) Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-H82E9 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, ,His Tag (SPR & BLI verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RI / CD64 | FCA-H52H1 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  | |
| FCA-H82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | ||
| CD4-M5227 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| CD4-M82E7 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | ||
| FCA-C82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RI / CD64 Protein, His,(MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b | CDB-M52H7 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| CDB-M82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDB-C5224 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein, His Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | ||
| CDB-C82E4 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIB / CD32b Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c | CDB-H5228 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| CDB-H5298 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H52S9 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein, HSA,His Tag (MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H82E0 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIB/C / CD32b/c Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a | CD1-H5223 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a (H167) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | |
| CDA-H5221 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a (R167) Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified)Hot |  | ||
| CDA-H82E6 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a (H167) Protein,,His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |  | ||
| CDA-R52H5 | HEK293 | Rat Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  | ||
| CDA-C52H7 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-C82E5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| CDA-R52H4 | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque Fc gamma RIIA / CD32a Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIII / CD16 | CDA-M52H8 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| FC6-M82E0 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | ||
| FC6-C52H9 | HEK293 | Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| FC6-C82E0 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His,(MALS & BLI verified) |  | ||
| FC6-R52H6 | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque Fc gamma RIII / CD16 Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) | CDB-H5227 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| CDB-H5296 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS & BLI-verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H82E4 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA1) Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) | CDB-H5222 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | |
| CDB-H5294 | HEK293 | Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) Protein, SUMO,His Tag (MALS & BLI-verified) |  | ||
| CDB-H82Ea | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIB / CD16b (NA2) Protein, His,(SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |  | ||
| Fc gamma RIV / CD16-2 | FC4-M52H3 | HEK293 | Mouse Fc gamma RIV / CD16-2 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  | |
| FC4-M82E8 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Mouse Fc gamma RIV / CD16-2 Protein, His,(BLI verified) |  |
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD23 | CD3-H5249 | HEK293 | Human CD23 / Fc epsilon RII Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  |
| CD3-H82Q5 | HEK293 | Biotinylated Human CD23 / Fc epsilon RII Protein, His,(MALS verified) |  | |
| Fc epsilon RI alpha | FCA-H5228 | HEK293 | Human Fc epsilon RI alpha Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  |
| FCA-H5259 | HEK293 | Human Fc epsilon RI alpha Protein, Fc Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |  |
>>> Why Fc Receptors Are So Important?
>>> Role of FcRn as a therapeutic target
References
1. Jerrard M Hayes, Mark R Wormald et al. Fc gamma receptors: glycobiology and therapeutic prospects. Journal of Inflammation Research. 2016, 9:209–219.
2. Bryan C Barnhart, Michael Quigley. Role of Fc–FcγR interactions in the antitumor activity of therapeutic antibodies. Immunology and Cell Biology. 2017, 95, 340–346.
3. Gestur Vidarsson, Gillian Dekkers. IgG subclasses and allotypes: from structure to effector functions. Frontiers in Immunology.2014, 5(520).
4. Sophie Siberil, Charles-Antoine Dutertre et al. FcγR: The key to optimize therapeutic antibodies? Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 2007, 62,26–33.
5. Xin Chen, Xiaomin Song et al. FcγR-Binding Is an Important Functional Attribute for Immune Checkpoint Antibodies in Cancer Immunotherapy. Frontiers in Immunology.2019,10.
6. Xu-Rong Jiang, An Song et al. Advances in the assessment and control of the effector functions of therapeutic antibodies. Nature Review, Drug Discovery.2011,10.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
