Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>

































> Insights > Interpreting the Association Between Cytokines and Autoimmune Diseases--Topic 1 Cytokines are a class of protein signaling molecules produced by cells of the immune system. They play an important regulatory role in immune responses and inflammatory processes.
1. Under normal circumstances, cytokines help the immune system recognize and eliminate pathogens while maintaining immune system balance.
2. When the immune system malfunctions, there may be issues with the production and regulation of cytokines, leading to the development of autoimmune diseases.
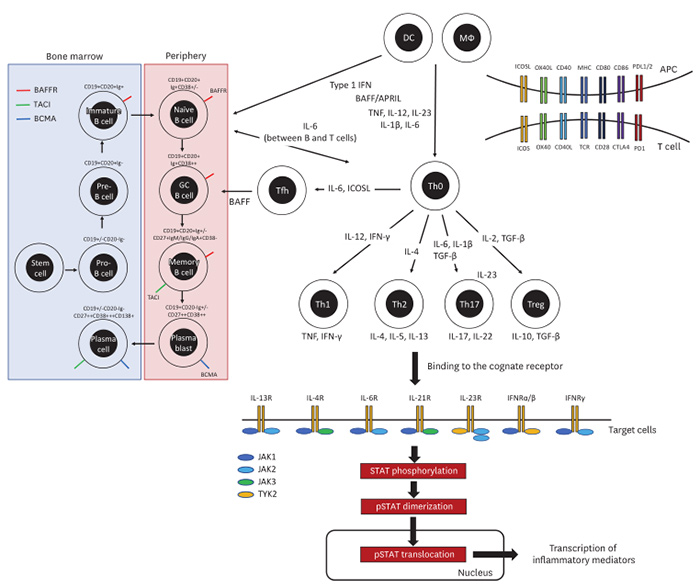
Key therapeutic targets in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
Rheumatoid Arthritis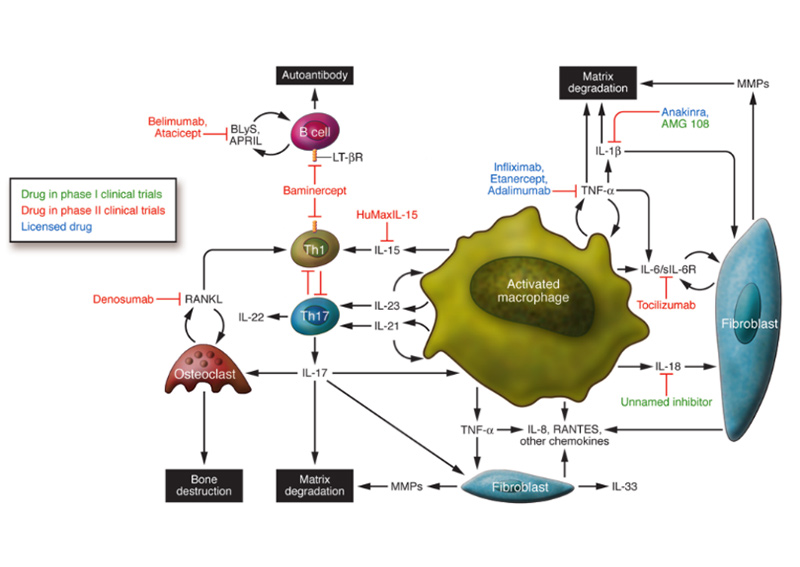
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus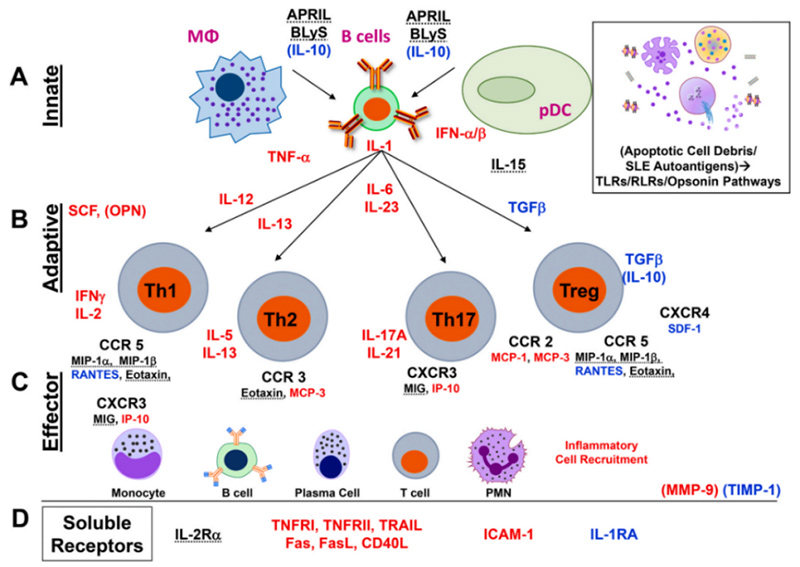
Multiple Sclerosis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly recognizes the body's own joint tissues as foreign invaders, leading to immune cell attacks on the joint tissues and triggering an inflammatory response.
The excessive production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) promotes the activation of inflammatory cells and joint destruction. Therefore, anti-TNF-α drugs such as infliximab, adalimumab, and certolizumab pegol are widely used in the treatment of RA.
In addition to TNF-α, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) also participate in the process of inflammation and joint destruction. Some drugs targeting IL-6 receptors, such as tocilizumab, and anti-IL-1 drugs like canakinumab, have been used for the treatment of RA.
Furthermore, interleukin-17 (IL-17) and interleukin-23 (IL-23) also play important roles in RA.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease caused by the deposition of autoantibodies and immune complexes that affects almost all organs of the body.
Increased production of type I interferon (IFN) activates immune cells, triggering inflammation and promoting SLE development. Emapalumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits IFN signaling, is used for treating adult SLE.
Elevated levels of IL-6 are associated with SLE activity and severity. Tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, is used for refractory SLE. IL-1 is involved in the pathogenesis of SLE, and Anakinra, an IL-1 inhibitor, has been tested for SLE treatment.
Increased TNF-α contributes to inflammation and immune cell activation. Infliximab, Etanercept, and Adalimumab are used for SLE treatment. IL-10 and TGF-β also play important roles in immune regulation in SLE, but there are no specific drugs for SLE treatment targeting them.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. In MS, various cytokines are involved in the activation of immune cells and the occurrence of neurodegeneration.
Research has found that granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor 2 (GM-CSF) is upregulated in patients with MS, leading to the activation and proliferation of immune cells, exacerbating inflammation, and potentially contributing to neurodegeneration.
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is overproduced in MS and can activate immune cells, leading to inflammation. TNF-α is another important cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of MS.
Interleukin-17 (IL-17), produced by Th17 cells, can induce inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) can enhance the function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and promote the excessive activation of the immune system.
Therefore, researchers are exploring the use of IL-2 as a treatment for MS to increase the number and function of Tregs and balance the immune response. Targeted therapies against these cytokines may alleviate inflammation and neurodegeneration, slow down MS progression, and improve patients' quality of life.
Understanding and intervening in the roles of various cytokines in autoimmune diseases is crucial for understanding disease mechanisms and providing effective treatment strategies. Targeted therapies target different cytokines have become an important strategy in treatment, offering hope and opportunities for improving patients' quality of life.
ACROBiosystems is providing you with a series of recombinant cytokines and their receptors, including Interleukins, Growth Factors, TNFs, Chemokines, CSFs, IFNs, and Complement Components with high purity, high bioactivity, and high batch-to-batch consistency to accelerate your autoimmune diseases drug development programs.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.