 Order Online! Now! Get your $50 coupon for online order.
Order Online! Now! Get your $50 coupon for online order. Order Online! Now! Get your $50 coupon for online order.
Order Online! Now! Get your $50 coupon for online order.
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
 Fill out organ-on-a-chip questionnaire to win a FREE gift!
Fill out organ-on-a-chip questionnaire to win a FREE gift!  Fill out organ-on-a-chip questionnaire to win a FREE gift!
Fill out organ-on-a-chip questionnaire to win a FREE gift!
> Insights > STAT3, the inescapable intersection of many carcinogenic signaling pathways Signal transduction and transcriptional activators (Signal transducer and activator of transcription, STAT) are a family of cytoplasmic transcription factors that bind to DNA and typically respond to a variety of extracellular cytokine and growth factor signals. After activation, it will be transferred from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and binds to specific sites of the target gene promoter sequence, promoting its transcription and participating in some important physiological processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, division, and differentiation. The members of the mammalian STAT family mainly include STAT1, STAT2, STAT 3, STA4, STAT5a, STAT5b, and STAT6. STAT3 and STAT5 are the convergence points of many oncogenic signaling pathways and have strong correlation with tumor progression and are considered as the next outlet for cancer treatment.
JAK (Janus kinase) is an important signal sensor for many cytokines, growth factors, and interferons. Under some stress response conditions, some cytokines bind to the corresponding receptors and induce the phosphorylation of Janus kinase and activate STAT3. The activated STAT3 dimer will then bind to specific DNA sequences, acting as a transcriptional regulator. At present, the most classic IL6 / JAK / STAT3 pathway has been confirmed to involve the target gene transcription related to the progression of breast carcinoma and induce chemoresistance in breast carcinoma.
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases such as SRC and ABL can also lead to the constitutive activation of STAT3. SRC can induce phosphorylation of tyrosine residues to activate STAT3, which promotes the transfer towards the nucleus and exercises gene transcription regulation.
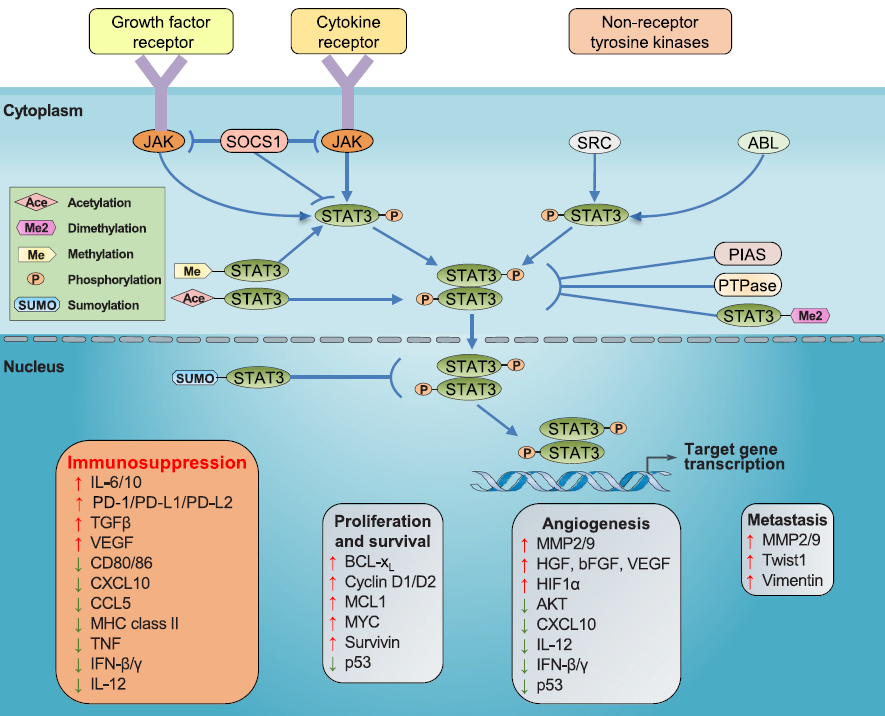
STAT3 signaling pathway
It has been found that STAT3 is overactivated in a variety of human cancers and is an important factor for tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME) signaling transduction and cancer progression as follow:
Induce TME Immunosuppressive: the increase of STAT3 in TME drives increased expression of immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, PD-L2, and CTLA-4, leading to the enrichment of Treg cells and B cells, as well as the polarization of M2 macrophages, resulting the immune evasion.
Reduce anti-tumor immunity: elevated STAT3 in CD8+ T cells, NK cells and neutrophils inhibit the lysis activity of anti-tumor cells. In addition, STAT3 can also inhibit the anti-tumor ability of dendritic cells by inhibiting their maturation, activation, and antigen delivery.
Promote tumor progression: STAT3 activation leads to increased secretion of immunosuppressive factors, such as IL-6, IL-10, and EGFR, activing TME-associated CAFs. The STAT3 in CAFs can promote tumor proliferation, survival, and migration, and promotes stroma remodeling and tumor development.
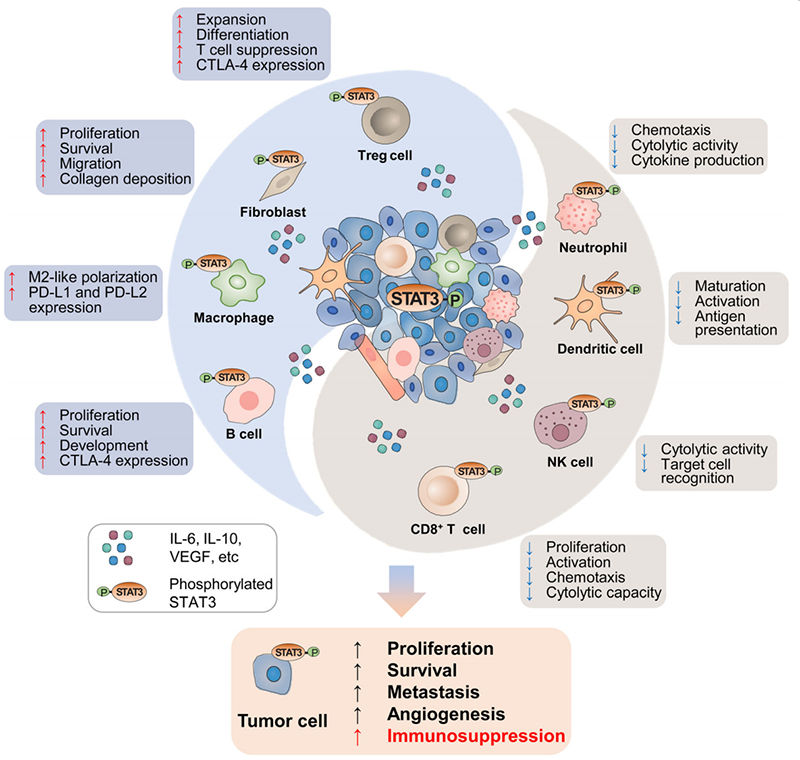
The mechanism of action of STAT3 in TME
STAT3 has been demonstrated by several studies as a cancer driver and modulator of the tumor microenvironment and becomes one of the most attractive targets in oncology and immune-oncology.
At present, STAT3 small molecule inhibitors can directly inhibit STAT3 by destroying the phosphorylation of STAT3 and inhibiting the formation of functional STAT3 dimers.In addition, there are also some inhibitors that indirectly inhibit STAT3 by blocking upstream signal paths such as EGF, VEGF, JAK, etc.
Combined immunotherapy targeting STAT3 is considered not only to improve anti-tumor efficacy but also to reduce tumor resistance. In addition, STAT3 inhibitors in combination with CAR-T cells can reduce the over-expansion of CAR-T cells, relieve cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and reduce the incidence of immune-related adverse reactions.
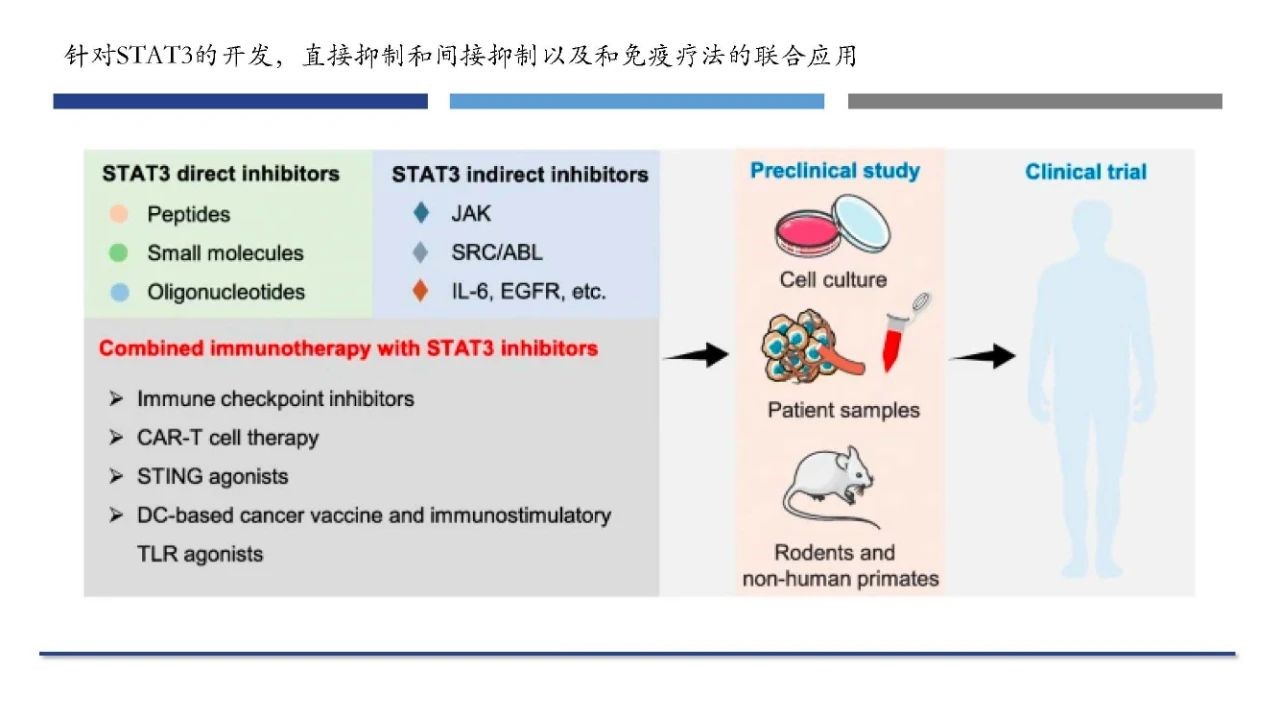
Targets STAT3 inhibitors and combination immunotherapy
Due to the ability to inhibit the target protein's function and block the target protein's expression, PROTAC has a strong drug efficacy and higher selectivity, making it a new idea to break the non-druggable of STAT3. On June 2, Kymera Therapeutics announced that its STAT3 protein-degrading agent KT-333 had been awarded orphan drug status by the FDA for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).

It has been demonstrated in several studies that STAT3 is overactivated in a variety of human cancers and plays a role as a cancer driver and tumor microenvironment regulator, making it became one of the attractive targets in oncology and immuno-oncology. Many STAT3 inhibitors have achieved remarkable results in vitro and in vivo, and some have been under clinical trials. In addition, PROTAC can be used as a new idea for the development of effective STAT3 inhibitors and has also broken the deadlock to obtaining orphan drug status. We believe that with growing research, we are looking forward to the development of STAT3 targeting drugs in the future.
To support the development of STAT3-targeted drugs, ACROBiosystems has developed a full range of products, aiming to provide a complete in vitro validation protocol for STAT3-targeted drugs from binding to functional assay.
Click on the molecule to view the product details
| STAT3 | JAK1 |
| IL-6 | IL-6 R alpha |
| EGF | EGF R |
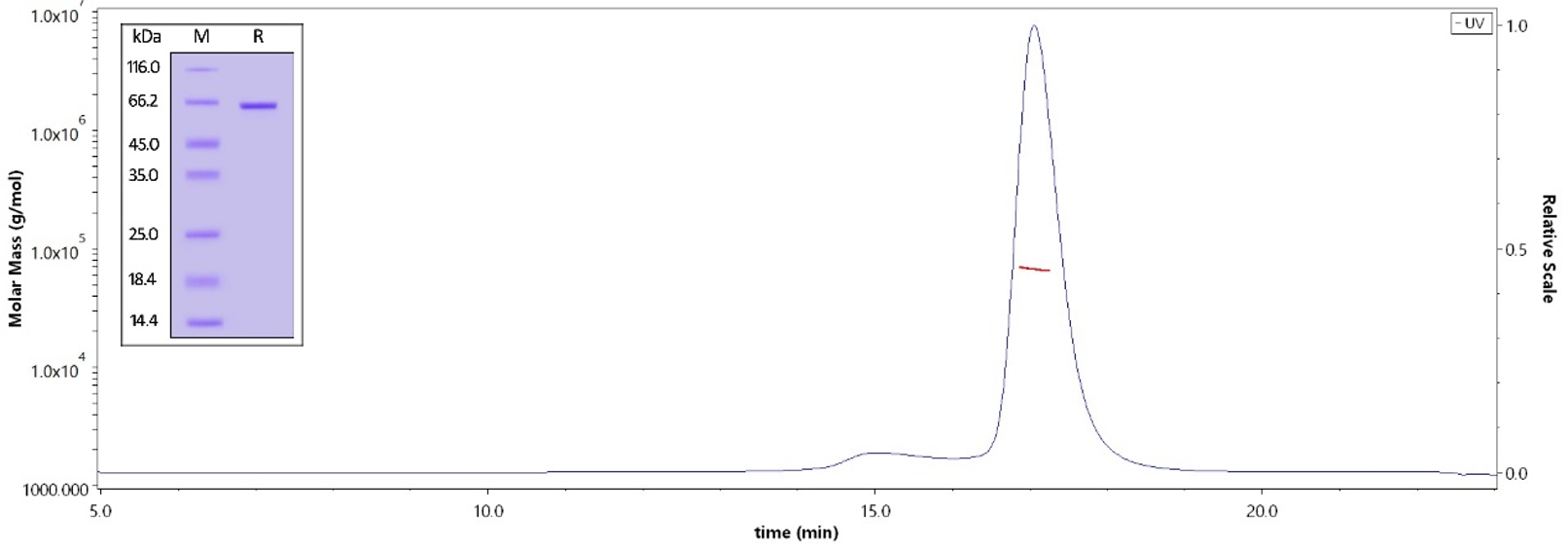
The purity of Human STAT3, His Tag (Cat. No. ST3-H5149) is more than 95% verified by SDS-PAG and greater than 90% verified by SEC-MALS. The molecular weight of this protein is around 60-75 kDa.
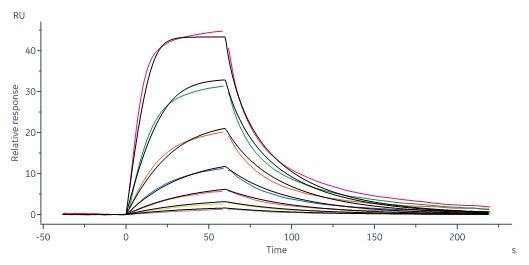
Human STAT3, His Tag (Cat. No. ST3-H5149) immobilized on CM5 Chip can bind STAT3 inhibitor with an affinity constant of 44.6 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (QC tested).
| Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|---|
| CHEK-ATF049 | EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell |
| CHEK-ATF047 | STAT3 (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell |
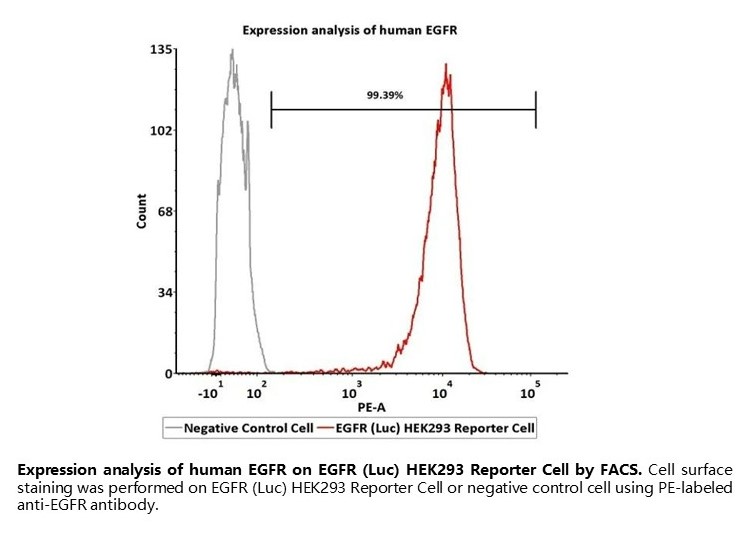
Expression analysis of human EGFR on EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell by FACS. Cell surface staining was performed on EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell or negative control cell using PE-labeled anti-EGFR antibody.
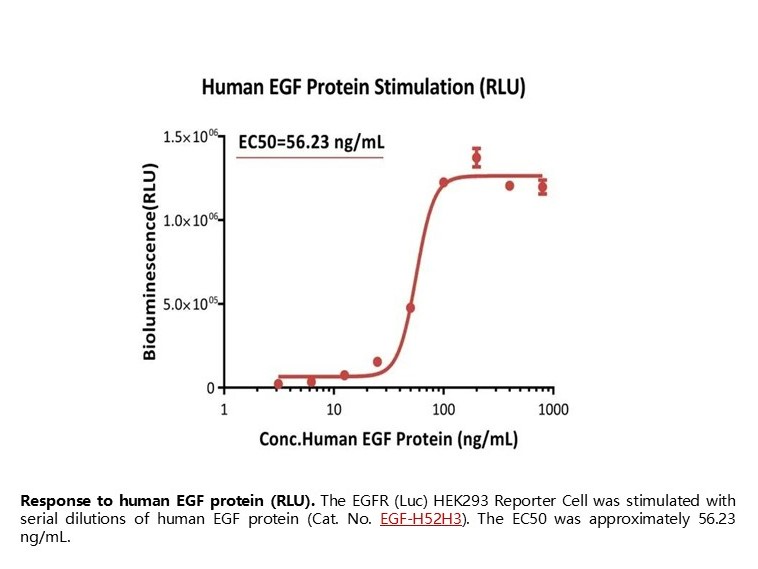
Response to human EGF protein (RLU). The EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of human EGF protein (Cat. No. EGF-H52H3). The EC50 was approximately 56.23 ng/mL.
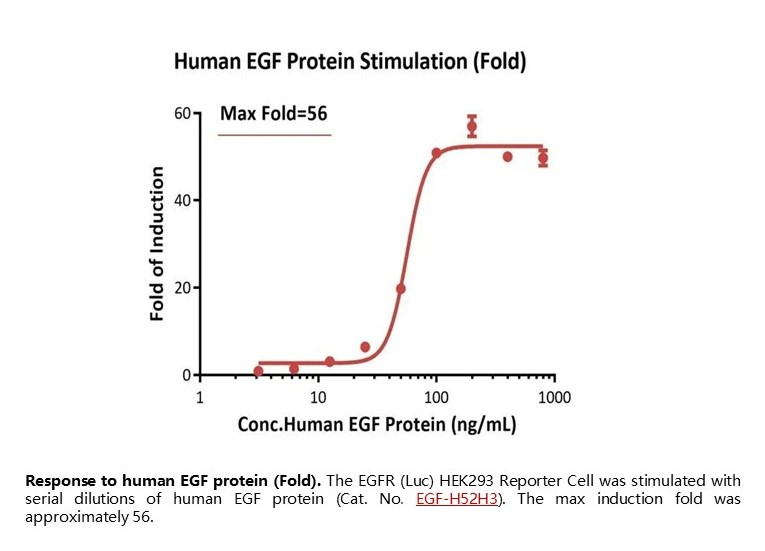
Response to human EGF protein (Fold). The EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of human EGF protein (Cat. No. EGF-H52H3). The max induction fold was approximately 56.
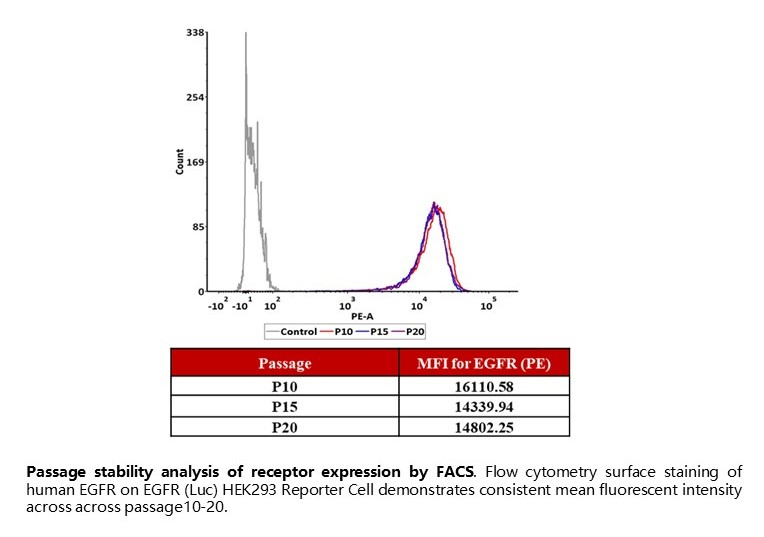
Passage stability analysis of receptor expression by FACS. Flow cytometry surface staining of human EGFR on EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell demonstrates consistent mean fluorescent intensity across across passage10-20.
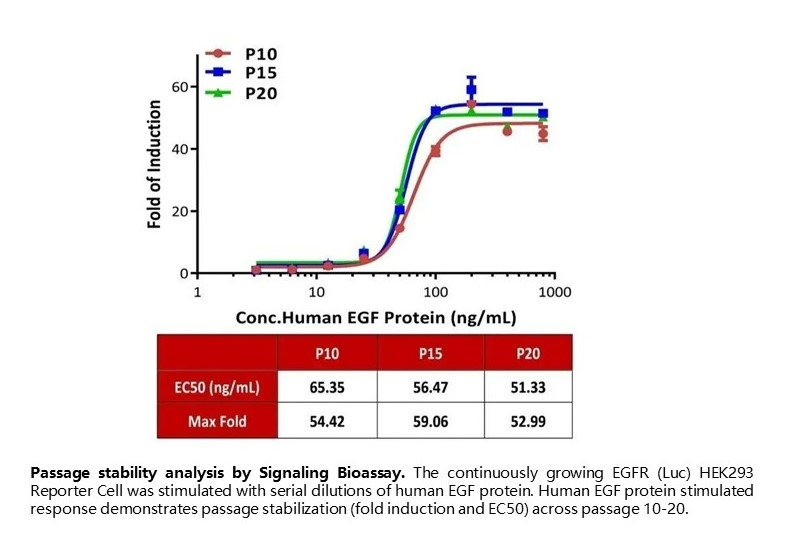
Passage stability analysis by Signaling Bioassay. The continuously growing EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of human EGF protein. Human EGF protein stimulated response demonstrates passage stabilization (fold induction and EC50) across passage 10-20.
| Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|---|
| MBE-K012 | Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) |
1. Wingelhofer B, Neubauer HA, Valent P, Han X, Constantinescu SN, Gunning PT, et al. Implications of STAT3 and STAT5 signaling on gene regulation and chromatin remodeling in hematopoietic cancer. Leukemia. 2018;32(8):1713-26.
2. Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y, Fu X. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):145.
3. He M, Cao C, Ni Z, Liu Y, Song P, Hao S, et al. PROTACs: great opportunities for academia and industry (an update from 2020 to 2021). Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):181.
4. Radi G, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, Diotallevi F, Molinelli E, Offidani A. Baricitinib: The First Jak Inhibitor Approved in Europe for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis in Adult Patients. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(11).
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
